When it comes to proxies, there are two main types: HTTP and SOCKS. What’s the difference between them? How do you choose which one is right for you? In this blog post, we will discuss the basics of HTTP and SOCKS proxies and help you decide which type is best for your needs.
HTTP proxies are used to access websites while hiding your IP address
SOCKS proxies, on the other hand, can be used for a variety of tasks such as hiding your location, accessing region-locked content, and even establishing a secure connection to a remote server.
While both HTTP and SOCKS proxies can be used to conceal your identity online, there are some key differences that you should be aware of. Here’s a closer look at the difference between HTTP and SOCKS proxies:
What is an HTTP Proxy?
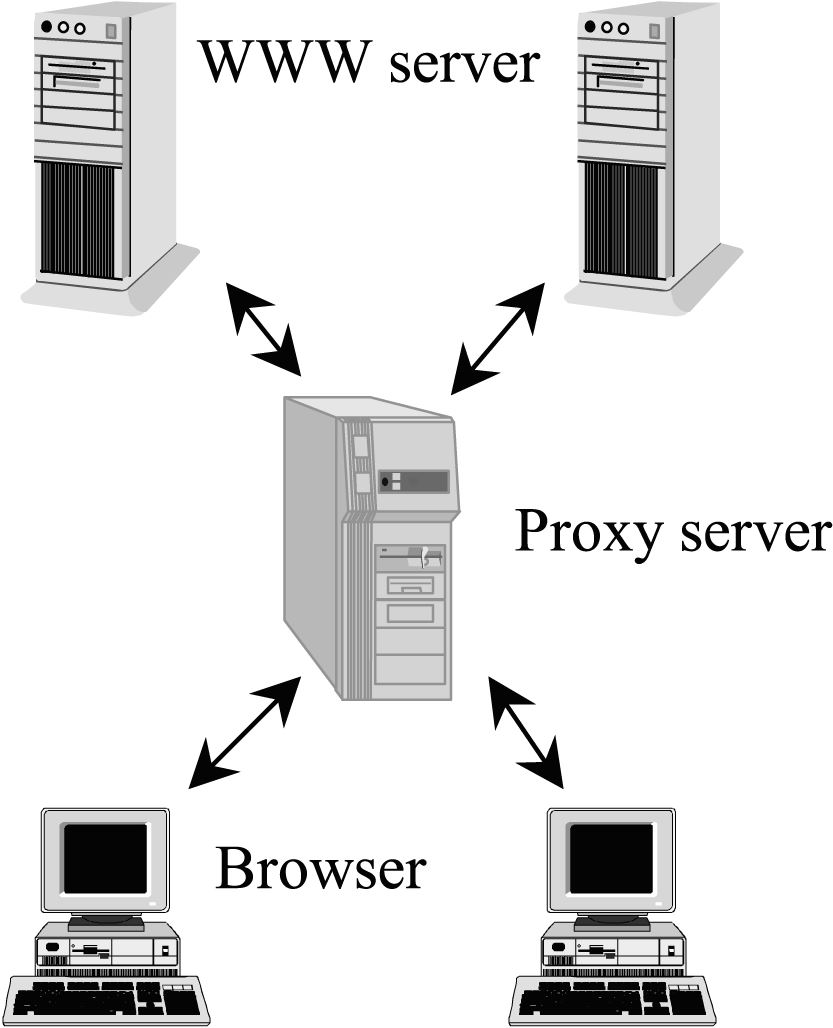
An HTTP proxy is a type of proxy server that handles hypertext transfer protocol (HTTP) traffic. When you connect to a website via an HTTP proxy, your computer will send a request to the proxy server which will then forward it on to the website’s server. The website’s server will then send the response back to the proxy server which will, in turn, forward it on to your computer.
SOCKS proxies are used to tunnel traffic through a remote server
Usually for the purpose of anonymizing your traffic. HTTP proxies, on the other hand, are designed to cache web content for faster loading times.
So, what’s the difference between an HTTP and SOCKS proxy?
An HTTP proxy is typically used to speed up web browsing by caching frequently accessed web pages. When a user requests a web page that is already in the proxy’s cache, the proxy server returns the cached copy instead of fetching the page from the website’s server. This reduces the amount of data that needs to be transferred, and can therefore improve page load times.
HTTP proxies are often faster, but can be blocked more easily than SOCKS proxies
HTTP proxies are commonly used to improve speed and performance. They do this by caching common resources that are requested by users. This can be a great benefit if you’re on a slow or congested network, because the cached resources will load faster than if they were being retrieved from the server each time. However, HTTP proxies can also be easily blocked by websites and networks.
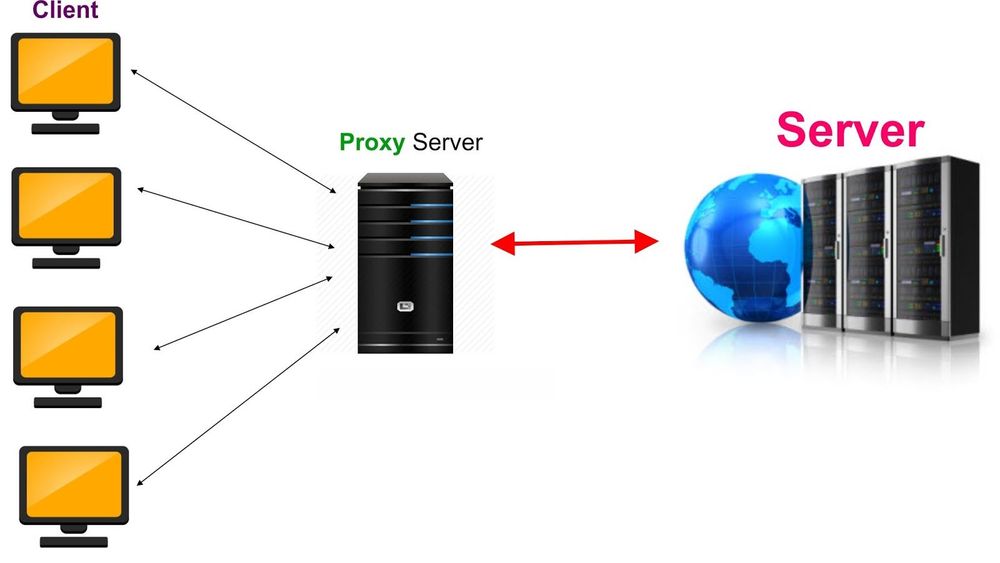
SOCKS proxies, on the other hand, are not as easily blocked. They work by routing your traffic through a different server, which can make it more difficult for websites and networks to block your access. SOCKS proxies can be slower than HTTP proxies, however, because they generally don’t cache resources.

MOST COMMENTED
finance
How to check if a proxy is datacenter or residential
finance
What’s the difference between a proxy and a firewall
finance
What’s the difference between an HTTP and SOCKS proxy
finance
Does a proxy hide your IP
finance
What a proxy name means
finance
How to connect through residential proxies
finance
Can residential proxies expire